Share
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)

Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease caused by the degeneration of upper motor neurons in the motor cortex and lower motor neurons in the spinal cord. The death or damage of motor neurons halts nerve signal conduction to muscles, stopping muscle function. ALS affects 2 in 100,000 people globally, and its incidence is increasing. In ALS, the neuromuscular system is affected, causing progressive muscle weakness. ALS symptoms vary from person to person, depending on which nerves are affected. Typically, ALS starts with muscle weakness in the hands, feet, arms, or legs, which worsens over time. The progression of the disease varies among individuals, but generally, people die within 2-3 years from onset due to neuromuscular respiratory failure.
ALS symptoms may include difficulties walking or performing everyday activities, tripping and falling, weakness in the legs, feet, ankles, or hands, slurred speech or trouble swallowing, muscle cramps and twitching in the arms, shoulders, and tongue, along with cognitive and behavioral changes. The cause of ALS is still unknown; however, 5-10% of cases have genetic origins, usually with an autosomal dominant hereditary pattern. Diagnosing ALS is challenging and is typically performed by excluding other diseases that mimic ALS.
Reference
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41573-022-00612-2
Cannabis and ALS
In 2004, a research group created an anonymous survey to assess the effect of cannabis on ALS. Among the 131 respondents with ALS, only 13 were using cannabis. Based on the responses from the cannabis-treated group, improvements were reported in symptoms such as appetite loss, depression, pain, spasticity, and drooling. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15055508/
The effect of cannabinol (CBN) was tested in an ALS mouse model. In this study, the authors observed an upregulation (increase) in endocannabinoid levels. Additionally, they delivered CBN using subcutaneous mini osmotic pumps (5 mg/kg/day) and observed a delay in disease onset, although the survival rate was not affected. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16183560/
There is a growing body of evidence that ALS causes neuropathic pruritus (severe skin itch sensation). A case report demonstrated the effect of cannabis on an ALS patient—a 60-year-old man with ALS and neuropathic pruritus. In this case, a cannabinoid product containing 2.43 mg of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and 2.75 mg of CBD in a capsule formulation was orally administered twice daily. The pruritus was assessed using a numeric rating scale ranging from 0 (no pruritus) to 10 (worst possible pruritus). Before the treatment, the man scored the pruritus at 7/10, and after 3 days of treatment, it decreased to 3/10. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/02692163211045314?rfr_dat=cr_pub++0pubmed&url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori%3Arid%3Acrossref.org
A real-world evidence study involving ALS patients with spasticity symptoms following treatment with a THC oromucosal spray containing 2.7 mg THC and 2.5 mg CBD, with varying numbers of actuations per day, reported high patient satisfaction with the THC treatment. https://bmcneurol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12883-019-1443-y#Sec38
Symptoms of the disease that cannabis can help
The most prominent symptoms of ALS are muscle weakness and spasticity. Several scientific articles demonstrate that cannabis can help reduce these symptoms. THC and CBD spray appear to be effective in reducing muscle spasticity and enhancing the performance of basic activities of daily living. Some reports also indicate a positive effect of cannabis in delaying ALS symptoms in rodent models. However, there are few studies investigating the effect of cannabis in humans. Despite the limited number of studies, the existing ones report a positive effect of cannabis in reducing muscle weakness and pruritus.
Evidence
(all of this evidence are described in the pharmacokinetics and symptoms part)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15055508
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16183560
https://bmcneurol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12883-019-1443-y#Sec38
Clinical trials
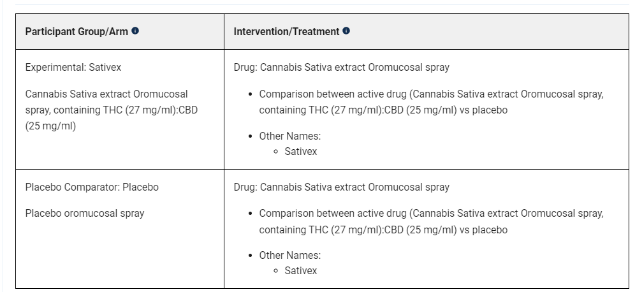
Phase II/III, completed – Safety and Efficacy on Spasticity Symptoms of a Cannabis Sativa Extract in Motor Neuron Disease (CANALS)
This study does not post the results.
Study plan
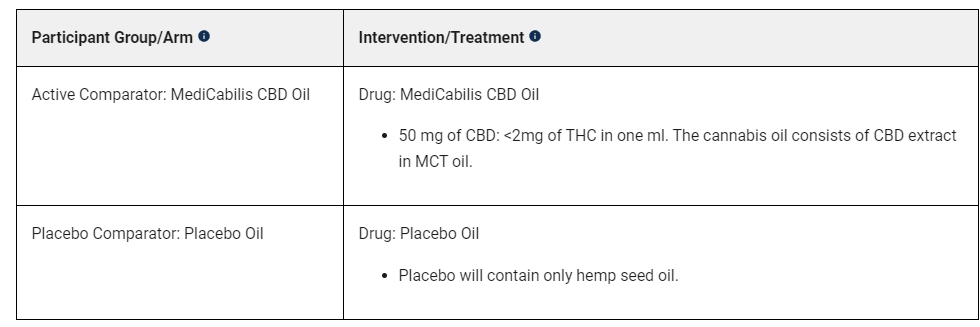
Phase III (MediCabilis CBD Oil), Active not recruiting – Efficacy of Cannabinoids in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis or Motor Neurone Disease
Results not posted
Study plan
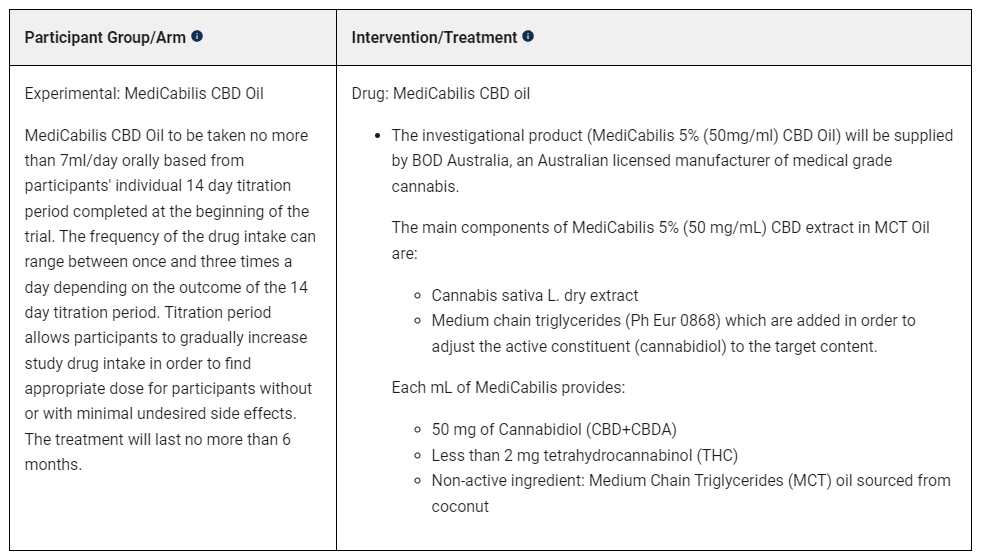
Phase IV (MediCabilis CBD Oil), Active not recruiting – EMERALD TRIAL Open Label Extension Study (EMERALD-OLE)
Results not posted
Study plan
Common Cannabis Treatment
Summing up, most ALS patients using cannabis-based medicines, describe an improvement of the symptoms post administration. According to the literature the most used method of delivery is an oil containing 2.7 mg THC and 2.5 mg CBD that can be administered via nasal spray or oral.
SOMAI offer a wide range of cannabis products that can be used by ALS patients for relief of their symptoms.
The preferred route of administration by ALS patients is the oral or nasal route, thus SOMAI soft capsules are recommended, for they allow a comfortable administration method and a precise dosage.
Oral solutions offered by SOMAI are a good choice for easy administration combining a large range of THC/CBD ratio.
For patients preferring nasal administration, SOMAI offers a nasal spray solution, providing a convenient administration with precise dosage and a balanced THC/CBD ratio. The spray offers a peppermint taste and fast onset of effects making it suitable for a quick relief. Moreover, oral sprays are compact and portable allowing patients to manage their symptoms in a convenient manner throughout the day.